The scope of practice of Medical Assistants depends on their clinical competency, education, and willingness of the employers to delegate clinical tasks. Some states do not provide precise regulatory guidance, while others may have specific guidelines.
This article covers the scope of the practice of Medical Assistants by State. It aims to help Medical Assistants (MAs) clarify their duties in various states while exploring opportunities.
Let us begin with a general understanding of the duties of MAs.
General Guidelines for Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
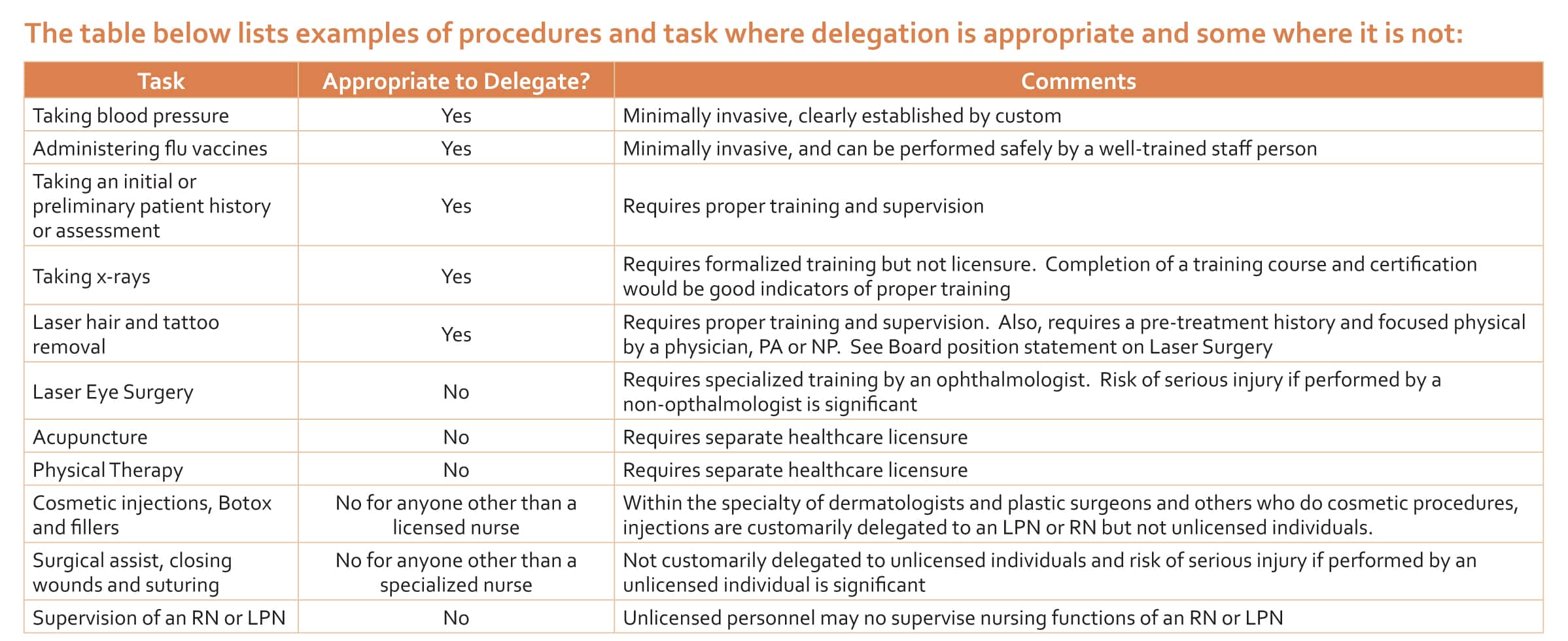
Competent and knowledgeable MAs can perform clinical tasks delegated by licensed physicians under their direct/onsite supervision. These tasks are:
- Repetitive (technical) and do not require specialized/complex skills, independent judgment, or a license.
- Having predictable outcomes.
- Can be safely performed without any threat to that patient.
- On non-critical patients.
- Customarily assigned to MAs in a similar practice.
Physicians may assign tasks directly/through licensed intermediaries like Licensed Practice Nurses (LPN), Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRN), Registered Nurses (RN), or licensed Physician Assistants (PA) unless specifically mentioned otherwise in the state-wise details.
Tasks that Medical Assistants May Perform
Most states allow MAs to perform the following duties (based on their competency) under the direct/onsite supervision of the delegating practitioners listed above:
- Measuring and recording vital signs
- Administering subcutaneous, intradermal, or intramuscular injections
- Venipuncture
- Educating and providing instructions to the patients
- Removing sutures from minor cuts
- Wound dressing
- Disinfecting treatment sites
- Preparing patients for examination
- Administering medications
- Administrative tasks (like billing, booking appointments, checkouts, insurance, routine follow-ups, etc.)
Unless specified hereafter, MAs perform these tasks in the state.
Tasks that Medical Assistants May Not Perform
Subject to the regulations and laws of the state, MA’s may not be allowed to perform the following duties:
- Examining the patient
- Performing Surgeries
- Invasive medical procedures
- Administering Anesthesia/anesthetic agents
- Operating laser equipment
- Interpreting test results
- Injecting medications into the vein
- Performing telephone triage
- Making medical care decisions
- Starting or discontinuing IVs
Unless specified henceforth, MAs in the state cannot perform these tasks.
Supervision Considerations
Most states hold the delegating practitioner responsible for the performance of delegated tasks. They become liable to face actions that medical licensing boards take against malpractice liability if medical assistants fail to provide appropriate care.
Employers must clearly define the scope of practice of MAs in the job description or policy.
Medical assistants can check the patient’s data; however, employers must check with the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services for their “meaningful use” requirements.
Unless mentioned otherwise, the supervisor is responsible for the actions/negligence of MAs.
We are now ready to explore state regulations for medical assistants.
Scope of Practice for Medical Assistant by State
| Select A State | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL | AK | AR | AZ | CA | CO | CT | DE | FL | GA |
| HI | ID | IL | IN | IA | KS | KY | LA | ME | MD |
| MA | MI | MN | MS | MO | MT | NE | NV | NH | NJ |
| NM | NY | NC | ND | OH | OK | OR | PA | RI | SC |
| SD | TN | TX | UT | VT | VA | WA | WV | WI | WY |
Alabama Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Alabama follows General Guidelines. Besides, the Alabama Board of Nursing allows registered/licensed nurses to take verbal/telephone orders for registered/certified MAs.
It is preferable to give a detailed written delegation.
Alaska Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Qualified medical practitioners in Alaska can delegate routine medical tasks (not requiring judgment or complex skills) to MAs if:
- The patient is assessed, stable, and non-critical.
- The MA is competent to and agrees to discharge the tasks.
- A comprehensive written delegation is provided for that patient only.
Arkansas Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Trained MAs in Arkansas assist licensed physicians in following clinical tasks under supervision.
- Non-invasive medical procedures.
- Primary healthcare tasks not requiring complex skills, etc.) after a qualified practitioner has examined the patient.
- MAs can administer medicines within the physician’s offices.
Arizona Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Arizona follows General Guidelines.
California Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
MAs in California:
- Must receive postsecondary and vocational education training from an accredited institution/authorized public school/or from a licensed medical service provider.
- Must complete the required hours of minimum training and demonstrate the same before administering medications through subcutaneous, intradermal, or intramuscular injections, performing skin tests, venipuncture, and taking blood samples.
- Can discharge technical support services under supervision.
- Cannot render inpatient care in licensed general acute care hospitals.
Colorado Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Colorado follows General Guidelines
Connecticut Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
AAMA and NHA list of certified MAs in the state of Connecticut indicates the MAs should certify to practice in CT as per the Connecticut Bill Amendments Sec. 47.
They can perform clinical procedures that can be safely done with known outcomes and do not require complex skills/judgment under supervision.
CMAs may administer vaccines after completing specific training requirements in non-hospital settings, under the direct supervision of licensed physicians.
They cannot perform radiography or give medicines through oxygen, immunizations, and tuberculin testing.
Delaware Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Delaware follows General Guidelines.
Florida Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Competent MAs in Florida can assist licensed practitioners under their direct supervision in the following clinical procedures.
Georgia Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Competent MAs in Georgia:
- Can take vital signs without supervision.
- Can administer subcutaneous and intramuscular injections, remove sutures, change dressings, and administer nebulizer treatments only if a licensed practitioner is present on the premises.
- Can perform delegated clinical tasks that do not require a license under appropriate supervision.
Hawaii Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Hawaii follows General Guidelines
Idaho Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Idaho follows General Guidelines
Illinois Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Licensed physicians in Illinois can delegate duties related to patient care to competent and trained MAs. The delegating physician must be present on the premises when MAs perform the delegated tasks.
The state reserves the right to formulate laws restricting delegation to operate light-emitting devices for patient care, indicating MAs may not operate them.
Indiana Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Indiana follows General Guidelines. MAs are also legally liable for negligence. Hence, it is advisable to take a comprehensive written delegation of tasks specifying the supervisor.
Iowa Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Licensed practitioners in Iowa can delegate safe clinical tasks to trained MAs working with them in inpatient and outpatient settings.
Insurance providers in IA cover negligence by MAs only if the delegation is in writing and includes
- Details of tasks and competencies needed.
- Tasks are delegable.
- Dates of competency assessment/re-assessment of MAs are specified.
- MAs perform them under the supervision of a registered nurse or physician.
Kansas Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Kansas follows General Guidelines, except that the delegation has to be directly from licensed physicians only.
Kentucky Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Competent MAs in Kentucky can perform basic clinical tasks delegated by a supervising licensed physician under direct/onsite supervision for outpatients.
The delegating physician can direct another competent provider (like registered nurses etc.) to supervise the MA.
As per the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, medication orders entered by credentialed MAs in CPOE (software) only qualify for Medicaid Incentive Program calculation.
MAs cannot order medicine refills (even if they meet protocols) for patients without prior approval/sign-off from the prescribing physician.
Louisiana Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Louisiana follows General Guidelines.
There are stringent laws regulating delegation to administer medicine to non-critical patients by Registered/advanced practice registered nurses to MAs in outpatient settings, including
- MAs must retrain/qualify this law governing the administering of medicine, even if they are trained/certified under some other statutes of the state of Louisiana.
- MAs cannot administer drugs through IV, blood/blood products, investigational drugs, cancer therapy drugs, controlled substances, anesthetic agents, total parenteral nutritional solutions, insulin, oxygen, or cosmetic/dermatological procedure agents.
Maine Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
The state of Maine considers MAs as physicians’ agents performing assistive clinical tasks under their direct supervision and authority.
Unless they have a valid license, they can only act as technicians in the office premises of optometrists and not assess/evaluate results.
Maryland Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Physicians in Maryland can delegate basic surgical and non-surgical tasks that do not constitute the practice of medicine to competent MAs under direct/onsite supervision.
The relevant statute enlists tasks that MAs can perform with and without supervision (page 3 point .04 onwards), including:
MAs cannot:
- Administer anesthetic agents or sedative substances of any kind, except for the topical local anesthetic application in small proportions.
- Examine/advise patients, dispense medicines, or give physical therapy.
- Initiate independent treatment, except for cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Maryland statutes hold the MAs legally responsible for any negligence/error. Both – the delegating physician and defaulting MA are liable to face the consequences mentioned therein.
Massachusetts Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Skilled MAs in Massachusetts can perform non-invasive medical procedures and patient care tasks under the supervision of delegating licensed physicians.
Certified Medical Assistants (CMAs) employed with the primary care provider and discharging delegated clinical/administrative tasks under direct supervision can be delegated immunizations. The delegating provider must be present on the premises, but need not be present in the immunization room.
Michigan Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Knowledgeable and competent MAs in Michigan can perform routine clinical tasks (including Influenza vaccinations) delegated by licensed physicians under their direct supervision.
Supervision includes continuous availability of the delegating physician through radio, telephone, or telecommunications, with the MA performing tasks.
MAs can communicate (without personal judgment/error) via electronic means (Telemedicine/Telehealth) with the delegating physicians if the written delegation describes tasks that can be electronically transmitted.
MAs can be delegated billable tasks under Chronic Care Management (code 99490), Transitional Care Management (code 99496), and CPT code 99495 for Medicare policy.
Minnesota Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Minnesota follows General Guidelines, except that the delegation has to be directly from licensed physicians only.
Mississippi Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Mississippi follows General Guidelines.
Missouri Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Missouri follows General Guidelines .
Montana Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Capable MAs working under licensed healthcare professionals can perform invasive procedures, IV administration of blood products/medication, conscious sedation monitoring, allergy testing, and administer injections (except immunizations), and other delegated patient care tasks under direct/onsite supervision of licensed providers in Montana.
The delegation shall include the names of the MAs and details of delegated patient care tasks. MAs must update the patients’ records.
MAs do not include healthcare professionals whose license has been relinquished/revoked for any reason, voluntarily or otherwise.
Nebraska Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
MAs/Certified Medical Assistants (CMAs) must be registered as Medical Aides in Nebraska to administer medicines.
MAs/CMAs need to clear an assessment after a 40-hour course to work in nursing homes, assisted living facilities, or mental retardation facilities.
MAs/CMAs employed in clinics and medical offices need to clear a competency test. They can perform safe clinical/patient care tasks under direct/onsite supervision of delegating licensed practitioners.
Nevada (NV) Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Trained MAs in Nevada can perform routine clinical tasks delegated by licensed physicians directly/through physician assistants (employed with the same licensed providers as the MAs) under their direct/on site supervision.
MAs can perform invasive procedures under the immediate supervision of the delegating physician.
MAs cannot administer an anesthetic agent.
Supervision includes remote supervision via phone/similar channels of MAs in rural areas under specified conditions (NAC 630.820 onwards).
New Hampshire Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Skilled MAs in New Hampshire can perform clinical tasks delegated by licensed physicians under their direct supervision. There are no specific rules.
New Jersey Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
CMAs (as defined by the NJ laws) may administer subcutaneous, intradermal, or intramuscular injections or perform venipuncture, as directed by licensed physicians after completing minimum hours of training and performing the minimum number of tasks of each type satisfactorily.
Delegating physicians must be present on the premises when MAs administer injections.
Certified MAs cannot inject local anesthetics, experimental drugs, controlled/dangerous substances, drugs not approved by the FDA, or substances related to allergic testing.
Competent MAs can perform clinical tasks delegated by licensed physicians under their direct/onsite supervision.
New Mexico Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Licensed physicians and nurses in New Mexico can delegate clinical tasks to competent MAs working with them under direct supervision.
New York Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
The published tasks that MAs can/cannot perform in the state of New York are demonstrative/inclusive.
Competent MAs can perform safe clinical and administrative tasks that do not require independent clinical assessment or a license under adequate supervision.
MAs in New York cannot administer medications, prepare/administer vaccinations, immunizations, or allergens, pull-up medications in injections, administer contrast dyes or injections of any kind, insert/remove IVs or catheters, communicate positive test results with patients, etc.
North Carolina Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Licensed physicians in North Carolina can delegate safe clinical tasks to competent MAs under direct supervision or the supervision of nurses.
Knowledgeable MAs can be delegated routine tele-screening in writing with detailed instructions by physicians.
Nurses (RN and LPN) can assign safe patient care tasks to competent MAs under appropriate supervision.
North Dakota Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Licensed physicians can delegate routine clinical tasks to competent MAs under direct/onsite supervision.
Nurses can delegate certain injections to qualified MAs registered as Medical Aides III.
Ohio Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Licensed physicians in Ohio can delegate safe clinical tasks to competent MAs under direct/onsite supervision.
Only certified CMAs can administer drugs as directed by nurses/physician assistants under supervision.
MAs/CMAs cannot administer anesthesia, controlled drugs, medications through IV, or initiate IVs.
Oklahoma Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Oklahoma follows General Guidelines.
Oregon Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Licensed physicians/physician assistants can delegate safe clinical tasks to competent MAs under direct/onsite supervision.
Pennsylvania (PA) Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Knowledgeable and competent MAs in Pennsylvania can be delegated clinical tasks (that can be safely performed) by licensed physicians under direct/onsite supervision.
Rhode Island Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Licensed practitioners (physicians, nurses, and physician assistants) can delegate clinical tasks to MAs based on their training or certification under direct/onsite supervision.
The delegation must be in writing and specify details of delegating supervisors and tasks.
Detailed guidelines provide tasks that MAs and CMAs can/cannot perform.
Regulations of employing licensed hospitals govern MAs working with them.
South Carolina Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Statutes of South Carolina specify tasks that MAs and CMAs can/cannot perform.
Licensed physicians can delegate clinical tasks to competent CMAs/MAs.
Nurses/physician assistants can delegate only if their agreements authorize the specified clinical tasks therein.
Delegating supervisors must be immediately available (but may not be in the same room) when CMAs/MAs perform the tasks.
South Dakota Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
There is no specific rule about licensed physicians delegating clinical tasks to MAs in South Dakota.
Nurses can delegate nursing tasks to certified MAs if the agency permits such delegation in the practice setting (including administering scheduled medications intramuscularly, intradermally, or subcutaneously and measuring the prescribed amount of medicine dose) under supervision.
CMAs cannot administer IV therapy.
Tennessee Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Tennessee follows General Guidelines.
Supervision includes immediate availability via phone/video call.
CMAs can be delegated COVID-19 vaccinations.
Texas Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Licensed physicians can delegate clinical tasks (including IV tasks) to qualified and competent MAs directly/through intermediaries like nurses, etc., under direct/onsite supervision.
The delegation to administer dangerous drugs must also comply with other relevant specific state/federal laws governing the drugs.
Nurses can delegate nursing tasks to competent MAs considering 5-Rights (tasks, MAs, situation, supervision, and direction/communication).
Utah Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Licensed physicians in Utah can delegate clinical tasks to competent MAs under direct/onsite supervision.
MAs cannot perform surgical procedures, administer anesthesia (other than local application during minor procedures), or prescribe medicines.
Vermont Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Skilled MAs in Vermont can perform medical care/treatment tasks delegated by physicians under direct/onsite supervision.
Virginia Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Virginia follows General Guidelines. Trained MAs can administer controlled substances under the direct supervision of licensed physicians except via intravenous, intrathecal, or epidural routes.
Washington Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
MAs must be accredited/certified to practice by the health department of Washington State.
CMAs can perform tasks listed under Section 18.360.050 delegated by licensed practitioners under supervision.
CMAs can remove IVs but not place them.
Delegating practitioners can supervise CMAs conducting telemedicine visits through audio/video technology. The supervisors must be immediately available on audio/video when CMAs perform offsite venipunctures/collect blood samples.
West Virginia Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Competent MAs having a national certification can administer routine medication to non-critical patients as delegated by registered nurses if the practice facility allows such delegation after verifying and documenting their competencies.
Licensed physicians can delegate safe clinical tasks to competent MAs directly/through intermediaries (like nurses, physician assistants, etc.) under direct/onsite supervision.
Wisconsin Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Wisconsin follows General Guidelines, except that the delegation has to be directly from licensed physicians only.
Wyoming Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
Wyoming follows General Guidelines.
How To Use This Article To The Fullest
We have relied on official communication(s)/website for each state. Since rules are subject to changes, we recommend you visit the site (https://www.aama-ntl.org/employers/state-scope-of-practice-laws) and conclude.
Most states do not mandate the certification of Medical Assistants. However, accredited certification and registration with national agencies improve career growth/income and widen the scope to perform clinical tasks.
Best wishes for your Medical Assistant journey!

Written by : Casey Gardner
Casey Gardner is both a healthcare support professional and an accomplished content creator. She has been working as a certified health care professional with marketable skills as a physician assistant, and a qualified medical assistant for last two decades. She has dedicated her nursing career to produce over hundreds of content pieces since 2001, and her work has been published both online as well as offline.